Piriton is an antihistamine medication commonly used to relieve allergy symptoms such as sneezing, runny or itchy nose, itchy or watery eyes, and itching of the throat or skin. While Piriton can be effective in treating allergies, it can also have side effects. Not everyone will experience these side effects, and some individuals may experience them to a lesser degree.
Common Side Effects of Piriton
- Drowsiness: One of the most common side effects of Piriton is drowsiness or sedation. This effect can be especially pronounced with the first few doses and may decrease with continued use. However, some people remain drowsy, which can impair their ability to drive or operate heavy machinery.
- Dry Mouth: Piriton can reduce saliva production, leading to a dry mouth or a sensation of dryness in the throat.
- Blurred Vision: Some individuals may experience blurred vision or difficulty focusing while taking Piriton.
- Constipation: Piriton can slow down bowel movements and cause constipation in some individuals.
- Difficulty Urinating: In rare cases, Piriton can cause urinary retention, making it difficult to urinate.
- Nausea and Upset Stomach: Some people may experience nausea, stomach discomfort, or an upset stomach.
- Dizziness: Dizziness or lightheadedness can occur, especially when standing up quickly from a sitting or lying position.
- Nervousness or Excitability: In some individuals, Piriton can have the opposite effect of drowsiness, leading to nervousness or excitability.
- Headache: Headache is a potential side effect, although it is less common.
- Increased Heart Rate (Tachycardia): Piriton may lead to an increase in heart rate in some individuals.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergic reactions to Piriton are rare but possible. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience symptoms such as hives, rash, itching, swelling, or difficulty breathing.
- Uncommon or Severe Side Effects: Although less common, Piriton use has been associated with more serious side effects such as confusion, hallucinations, and seizures. If you experience these or any severe side effects, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
What is Piriton?
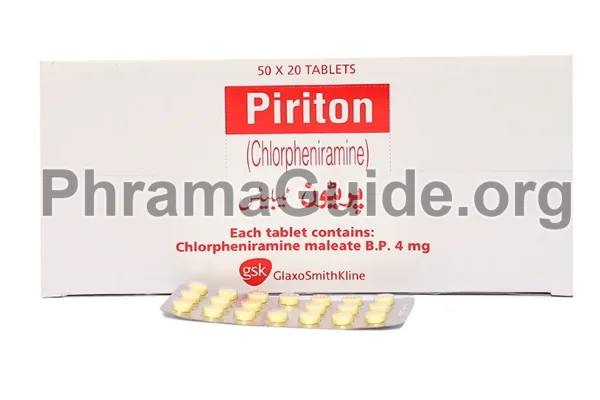
Piriton is one of the leading brands of Chlorpheniramine, manufactured and marketed by Glaxosmithkline Pharmaceuticals Ltd (GSK).
Piriton : Available Formulations and Strengths
Presently, Piriton is available in Tablet and Syrup forms.
Piriton Tablet : Chlorpheniramine 4mg strength.
- Chloropheniramine 2.5mg/5ml
- Sodium Acid Citrate 55mg/5ml
- Ammonium Chloride 125mg/5ml
- Glycerin 750mg/5ml strengths
What Are The Possible Drug Interactions of Piriton?
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants: Combining Piriton with other CNS depressants, such as alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, or sleep aids, can increase drowsiness and impair cognitive and motor skills. It’s essential to avoid alcohol and use caution when combining Piriton with these medications.
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs): MAOIs, a class of antidepressants, can interact with Piriton, leading to an additive anticholinergic effect and an increased risk of side effects. This combination is generally avoided.
- Other Antihistamines: Concurrent use of multiple antihistamines, including Piriton, can lead to an increased risk of side effects, such as excessive drowsiness and anticholinergic effects.
- Anticholinergic Medications: Piriton has anticholinergic properties. Combining it with other anticholinergic drugs, such as certain antidepressants, antipsychotics, or medications for overactive bladder, can lead to additive anticholinergic effects, resulting in dry mouth, blurred vision, constipation, and cognitive impairment.
- Amphetamines: The use of Piriton with amphetamines (e.g., for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder) may increase the risk of side effects, such as increased heart rate and blood pressure.
- Serotonergic Medications: Combining Piriton with serotonergic medications, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) or serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), may increase the risk of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition characterized by symptoms like confusion, agitation, rapid heartbeat, and high blood pressure.
- Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs): Piriton can enhance the anticholinergic effects of TCAs, potentially leading to a greater risk of dry mouth, constipation, and other side effects.
- Urinary Alkalinizing Agents: Medications that alkalinize the urine may reduce the excretion of Piriton, potentially increasing its blood levels and the risk of side effects.
- Medications that Affect Liver Enzymes: Some medications that affect liver enzymes, such as certain antifungal drugs and antibiotics, may alter the metabolism of Piriton. Dose adjustments may be needed in some cases.

Leave A Comment